Calculate your leave encashment in a click! Know the detailed Leave encashment received from your employer.
Home » Resources » Calculators » Leave Encashment Calculator 2026
| Particulars | Amount |
|---|---|
| Last drawn Basic Salary + DA | ₹ 0 |
| Unutilised leave after retirement | 0 leave |
| Leave Encashment recieved | ₹ 0 |
A Leave Encashment Calculator is an online tool that helps you calculate how much money you will receive for your unused earned leaves. Instead of manually applying formulas, the calculator instantly shows:
Encashment amount
Taxable amount
Tax-exempt amount
Total leave salary
It uses your basic salary, number of accumulated earned leaves, and leave encashment rules to give you an accurate estimate.
Leave encashment refers to the amount an employee receives for unused earned leaves. These leaves can be encashed during employment, at the time of resignation, retirement, or termination as part of the Full and Final Settlement (FnF).
In simple words, leave encashment means getting paid for the earned leaves you did not use.
If you come across terms like leave encashment meaning, leave salary, encashment of earned leave, or leave encashment on retirement – understand that all of these relate to payment for unused statutory leaves.
Type of Leave | Description ( varies across companies) | Encashment Eligibility |
Short-term leave used for personal reasons. | Often eligible for encashment, varies by company. | |
Earn leave / Privilege leave | Pre-approved leave for personal or professional purposes. | Eligible after a certain period. |
Leave taken for health reasons. | Short-term leaves may be encashed; long-term are not. | |
Paid leave for skill development through courses or certifications. | Often reimbursed and eligible for encashment. | |
Holiday Leaves | Paid leaves for holidays declared by the organization. | Generally eligible for encashment. |
Leave for pregnant employees, spanning 12-26 weeks. Extended leaves are not eligible for encashment. | Standard leave period is paid and encashable. |
The Leave encashment formula is as follows:
Leave Encashment = Unused Leave Days × Daily Salary*
*Daily Salary = (Basic Salary + Dearness Allowance) ÷ 30
Mr. X is retiring after “15 years” of service.
Daily Salary = ₹30,000 ÷ 30 = ₹1,000
Leave Encashment = 175 days × ₹1,000 = ₹1,75,000
The leave encashment calculator simplifies the process.
Step 1: Enter the basic salary and dearness allowance.
Step 2: Enter the number of earned leaves available.
Step 3: The calculator displays the amount of leave encashment.
Leave encashment is taxable, but the tax implications can vary based on the type of employee and the circumstances under which the leave encashment is received. For public sector employees, leave encashment is fully exempt from tax, providing a significant benefit at the time of retirement.
On the other hand, for private employees, leave encashment is partially taxable. The current tax exemption limit for private employees is set at ₹25,00,000. To claim tax relief, private employees can utilize Section 89 of the Income Tax Act and must fill out Form 10E. Understanding these tax implications can help employees plan better for their financial future and make informed decisions about their leave encashment.
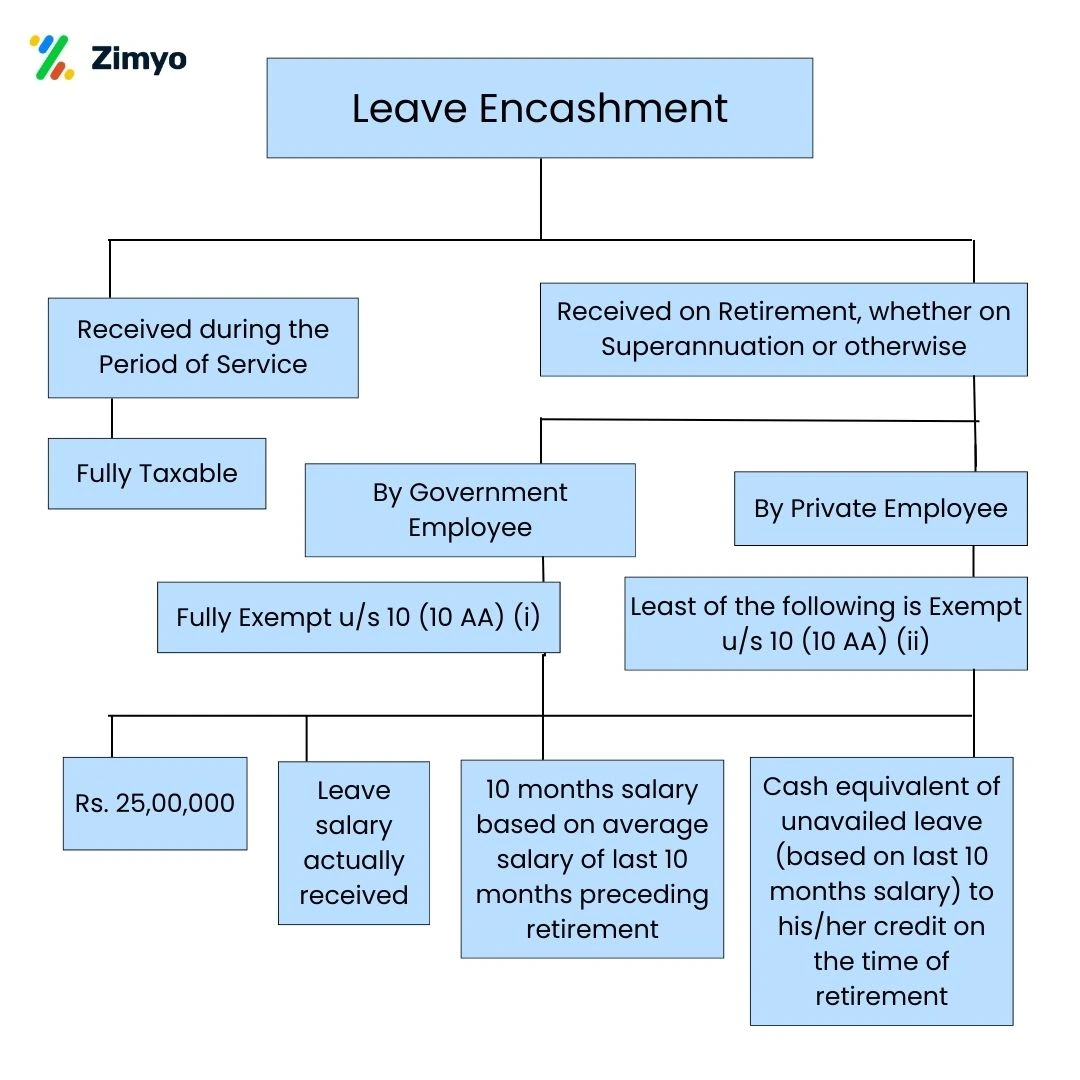
Under Section 10 AA of the Income Tax Act, earned leave encashment cannot exceed 30 days for every year of service. Taxability depends on:
When any kind of leave is encashed by the employee one can avail certain partial and full exemptions. The conditions of exemptions are:
To make the most of your leave encashment, consider these tips:
Check your company’s leave policy: Every organization has different rules regarding leave encashment.
Plan your leaves wisely: If your employer offers encashment at the end of service, ensure you collect leave accordingly.
Understand tax implications: Being aware of tax exemptions can help you optimize your financial benefits.
Understanding your company’s leave encashment policy is crucial for effective leave and financial planning. Each organization may have different rules, so it’s important to be aware of your specific company’s policy to make the most of your leave benefits.
Whether you’re encashing leave while in service or at retirement, knowledge of the leave encashment formula and taxability can help you make better financial decisions. Use a leave encashment calculator to estimate your benefits and plan accordingly.
A Leave Encashment Calculator makes it easier to understand how much money you can receive for your unused earned leaves. Instead of manually applying the leave encashment formula, the calculator instantly shows your leave salary, taxable amount, and exemption eligibility based on current rules. Whether you are planning to resign, retire, or simply encash leaves during service, having clarity on your leave encashment calculation helps you make smarter financial decisions.
By knowing the rules, understanding taxation, and keeping track of your earned leaves, you can maximize your benefits without confusion. Use the calculator to stay informed, plan ahead, and get the most value out of your accumulated leaves.
Leave encashment is calculated by multiplying your per day basic salary with the number of unused earned leaves.
To calculate encashed leaves, divide your monthly basic salary by 26 to get per day salary and multiply it with the total earned leaves you want to encash.
Yes, leave encashment is taxable except in the case of government employees who receive full tax exemption at retirement.
The new rule increases the tax exemption limit for private sector employees to 25 lakh under Section 10(10AA).
The formula for leave encashment is Basic Salary divided by 26 multiplied by the number of earned leaves.
“I was able to implement the platform on my own. It helps in assigning the tasks to other employees, conducting surveys & polls & much more. The ease of use & self-onboarding is something that I would like to appreciate.”


