Casual Leave (CL) is one of the most commonly used leave types in India. In most cases, employees take it for sudden, unexpected, or short personal reasons. Since these situations come without warning. As a result companies allow CL so employees can handle urgent matters without worrying about salary cuts or job issues.
With that in mind in this long-form guide, we will cover everything you need to know including casual leave meaning, casual leave rules, CL leave full form, common casual leave reasons, how to write a good CL application, and how CL compares with other leave types.
Now that you have an overview let’s explore each section in detail.
What is Casual Leave Meaning ?
To begin with, what is Casual Leave?
Casual Leave is a type of leave granted to employees for short, unplanned, or urgent needs. It is meant for situations where the employee cannot predict or plan the event in advance.
The CL leave full form is Casual Leave.
Purpose of Casual Leave
The main purpose of CL is to help employees manage unexpected personal matters without losing pay. Additionally, it also supports employee well-being by giving them the freedom to step away when life requires immediate attention.
For this reason most companies allow employees to take CL in small durations, usually 1 day or even half-day, depending on the situation.
Types of Casual Leave
1. Half Day Casual Leave
Sometimes, employees don’t need a full day off. Half day leave lets them take time off for part of the day. They can choose to leave during either the first half or second half of their working hours.
Example: Going to a doctor’s appointment, attending a parent-teacher meeting, or visiting a bank.
2. One Day Casual Leave
A single casual leave day is the most common type. Employees use it for personal tasks or simply to take a short break.
Example: Managing household chores, attending a family event, or running urgent errands.
Common Reasons for Taking Casual Leave
Reason for Casual Leave | Explanation |
Sudden illness | Used when the employee develops a fever, cold, headache, or minor health issue that needs immediate rest or medical attention. |
Medical appointments | Taken for doctor visits, check-ups, tests, or follow-up treatments that cannot be scheduled outside working hours. |
Urgent family matter | For situations like family emergencies, helping a family member, or attending to unexpected household needs. |
Home repairs or maintenance | Used when plumbers, electricians, or service workers visit and the employee must stay at home for supervision. |
School-related work | Needed for parent-teacher meetings, school fee submissions, or urgent academic matters for children. |
Important personal work | Covers banking tasks, legal documentation, government office visits, or other essential tasks requiring presence. |
Unexpected travel | For sudden out-of-town requirements such as family functions or urgent personal commitments. |
Vehicle breakdown | Taken when the employee’s vehicle stops working and they need time for repairs or alternate travel arrangements. |
Attending ceremonies | Used for weddings, engagements, funerals, or religious functions that arise unexpectedly. |
Urgent household responsibilities | For grocery emergencies, managing domestic staff issues, or unexpected responsibilities at home. |
Casual Leave in the Indian Workplace
Casual Leave meaning is widely used across Indian companies. While almost all organizations provide CL, the number of days and rules may vary.
A few key points about CL in India:
- Most companies offer 6 to 12 CL days every year
- Some states define their own CL rules
- Private organisations may set their own policy
- Casual leave is usually not carried forward to the next year
- It is generally used for urgent one-day or short-duration leave needs
Because workplaces in India deal with diverse needs, casual leave ensures employees can take time off without stress.
How to Write a Casual Leave Application
Writing a casual leave (CL) application is simple. The main purpose is to inform your manager in advance and clearly explain why you need leave. A good leave application should include:
1. A clear subject line: This helps your manager understand the purpose of your email immediately.
2. Reason for taking casual leave: Keep the reason short, clear, and honest.
3. Leave dates: Mention the exact date or duration of leave to avoid confusion.
4. Work handover details: If needed, mention how your tasks will be managed during your absence.
5. Contact information (optional): Add this if you want your manager to reach you for urgent matters.
6. A polite closing line: End the application with a respectful request for approval.
Professional Sample Casual Leave Application
Subject: Request for Casual Leave on [Date]
Dear [Manager’s Name],
I hope you are doing well. Today, I am writing to request casual leave on [date or dates] due to [mention your reason briefly — for example, a personal errand, urgent work at home, or a family matter].
Also, will complete all my pending tasks before the leave. I have also informed [colleague’s name, if applicable] to manage any urgent work during my absence.
Kindly approve my request for casual leave. I will be available on phone/email if there is anything urgent.
Thank you for your understanding.
Warm regards,
[Your Name]
[Your Job Title]
Rules of Casual Leave in India - You Should Know
Understanding how Casual Leave works helps employees use it correctly without any confusion. While every company has its own policy, most organisations in India follow some common guidelines. Below is an easy-to-read explanation of the key rules related to CL.
Rule / Aspect | Explanation |
Total Number of CL Days | Most companies provide 7–12 days of casual leave each year. Employees usually take these in short breaks of 1–3 days. |
How CL is Credited | Organisations may add CL monthly, quarterly, or once a year. For example, employees may receive 1 CL per month or the entire 12 days at the start of the year. |
Carry-Forward Policy | Casual leave generally does not carry forward. Any unused CL expires at the end of the year. |
Encashment | Unlike earned leave, CL cannot be encashed. Employees cannot convert unused CL into money. |
Notice Requirement | Most companies ask for 1–3 days’ prior notice, unless the reason is sudden, such as illness or emergencies. |
Supporting Documents | For 1–2 days of CL, documents are usually not required. A medical certificate may be needed if the leave extends beyond 2–3 days. |
Permitted Reasons | CL is meant for personal needs like minor health issues, family functions, urgent errands, or last-minute travel. |
Combining CL with Other Leaves | Many organisations do not allow combining CL with earned leave or sick leave. Some also restrict clubbing CL with weekends or holidays. |
Approval Conditions | Casual leave generally needs the manager’s approval. In true emergencies, employees may inform the manager later. |
Duration Allowed at Once | CL is normally taken for half a day to 3 days. Longer leave may need to be shifted to EL or SL. |
During Probation | Some companies either reduce CL for probationers or do not allow casual leave until the employee is confirmed. |
Government vs. Private Sector Rules | Government employees usually get 12 days of CL with uniform rules. Private companies follow state labour laws and may vary in their policies. |
Difference Between Casual Leave and Earned Leave
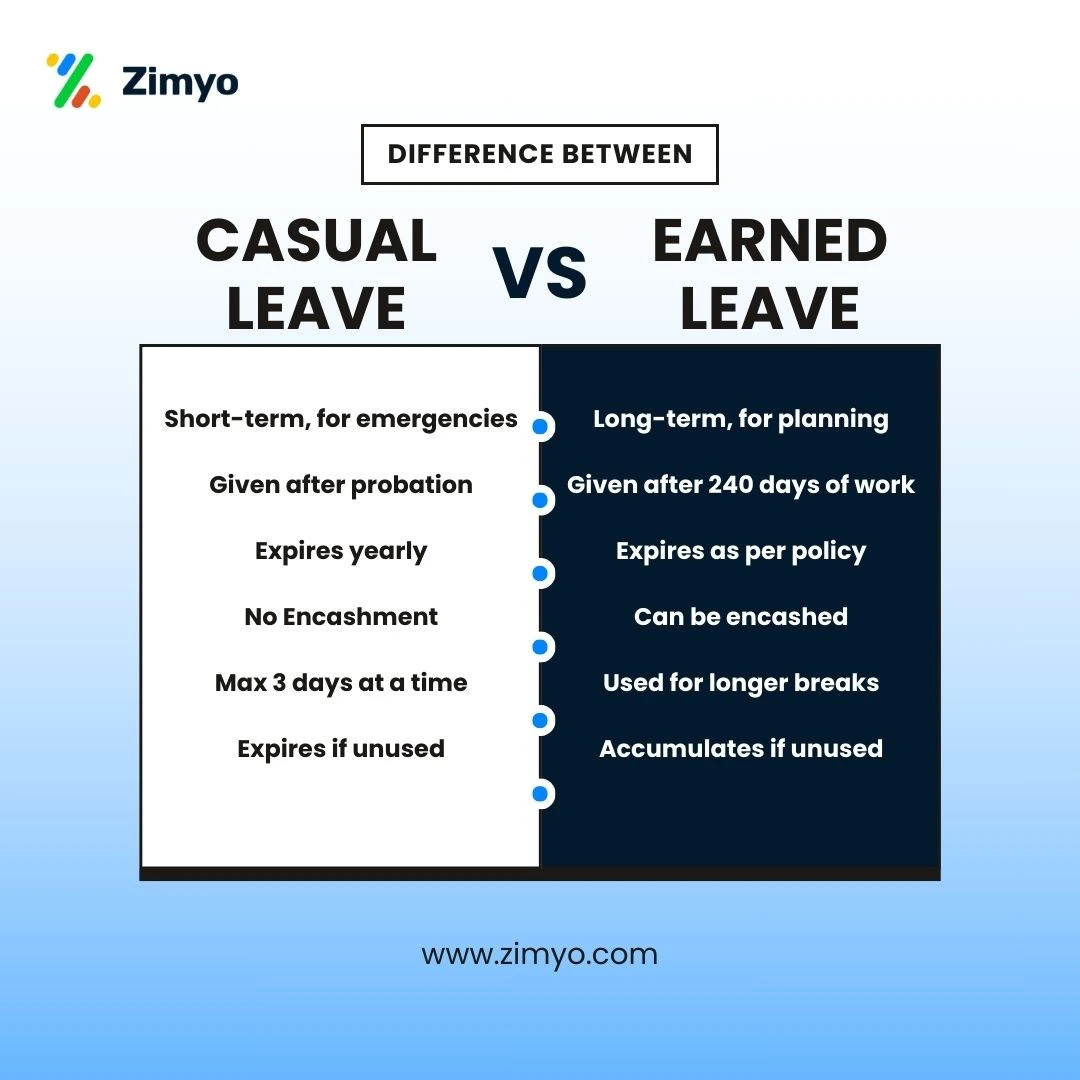
Here’s a clear detailed tabular representation of the difference between Casual Leave (CL) and Earned Leave (EL):
Aspect | Casual Leave (CL) | Earned Leave (EL) |
Purpose | Taken for short-term personal or emergency situations. | Accumulated for planned vacations or long-term needs. |
Eligibility | Available to employees after completing the probation period. | Granted after completing 240 days of service in a year. |
Carry Forward | Usually, it cannot be carried forward to the next year. | Allowed to carried forward based on company policy. |
Leave Encashment | Not encashed. | Can be encashed as per company policy. |
Approval Requirement | Requires prior approval in most cases, except in emergencies. | Requires approval and advance notice. |
Duration | Short-term, usually up to 3 days at a time. | Long-term, used for extended breaks. |
Paid Leave | Yes, casual leave is usually paid time. | Yes, earned leave is paid. |
Lapse Policy | Expires at the end of the year if not used. | Could be accumulated and used later. |
Combination with Other Leaves | It cannot be combined with earned or sick leave. | Can be combined with other types of leaves. |
Legal Provision | Regulated under company policies and labor laws. | Mandatory under labor laws in many countries. |
Importance of a Leave Management System
Handling different types of leave manually can be confusing and time-consuming. A Leave Management System makes it easy for employees to apply for leave and for HR teams to track and approve them quickly. It helps avoid mistakes, ensures fairness, and keeps the company compliant with leave policies.
With the best Leave Management System, businesses can prevent scheduling conflicts and reduce paperwork. Popular HR software like Zimyo offer automated leave management. Thus, making the process smooth and hassle free. Using an LMS saves time and helps companies manage employee leaves more efficiently.
Conclusion
Casual Leave is an essential benefit that supports employee well-being and work-life balance. As a result it allows employees to handle urgent personal matters without stress. To make the most of it, by understanding casual leave meaning, CL rules, allowed duration, and the right way to write a CL application, employees can use their leave responsibly and confidently.
From the employer’s perspective, companies also benefit because clear CL policies create a smoother workflow, fewer disruptions, and better communication. When used correctly, casual leave supports both employees and employers, leading to a healthy and productive work environment.
“A well-balanced leave policy keeps employees happy and productive!”
Do you have any questions about casual leave? Find answers in our FAQs section!
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the casual leave?
Casual leave meaning is a type of leave employees can take for short and urgent personal needs. It is usually taken for unplanned or sudden situations.
What are the rules for CL?
Rules for CL depend on company policy, but generally employees get a fixed number of days per year, cannot combine Casual leave with long leave types, and must take it in short durations.
Do casual staff get leave?
Yes, casual staff may get leave based on the organisation’s policy and local labour laws, but the number of days can differ.
How many CL are allowed?
Most companies allow around 6 to 12 casual leave days in a year, depending on state laws or company rules.
Can I take 7 days casual leave?
Casual leave is usually meant for short breaks, so taking 7 consecutive days is not allowed in most organisations.
Who is eligible for CL leave?
All regular employees are generally eligible for casual leave, but the exact rules depend on company policy and state labour regulations.




