In every workplace, feedback is like the steering wheel of a moving car. Without it, you might keep going, but you’ll probably drift off course. Every time you celebrate someone’s success, address challenges, or guide growth, feedback is a vital part. It allows you of build productive relationships and achieving company goals.
Yet here is where many businesses struggle. Because they either give too little feedback, or give it at the wrong time, or wrong way. That is why knowing the different types of feedback and when to use them is important.
In this guide, we’ll break down the types of feedback, explore how they work in real corporate settings, look at examples (including an example for negative feedback), discuss HR involvement, and show how HR software can make the process smoother and more effective.
Feedback Meaning
What is feedback? At its core, “feedback means sharing information about someone’s performance, behavior, or results so that they can understand what’s working and what needs improvement”.
No, it’s not about pointing out mistakes only, good feedback contains:
- Boosting up confidence
- Encourage better work habits
- Aligning employees with company goals
- Building stronger working relationships
Feedback can come in many ways formal or informal, positive or negative, self-reflective or peer-driven. The magic lies in choosing the right type for the situation.

Types of feedback
1. 360-degree feedback
The modern performance review method is gaining attention like a forest fire. Included in this process is confidential, anonymous feedback from the people who work around an employee. They can be the employee’s manager, colleagues, clients, superiors, etc.
Organizations today use 360 degree feedback software to learn and understand the strengths and weaknesses of an employee. Here superiors can evaluate an employee’s performance through multiple sources, instead of just one-on-one feedback from their direct manager.
360 degree feedback fosters an environment of transparency in the organization. Moreover, it boosts the overall performance of the team and facilitates self-awareness.
2. Constructive feedback
The idea behind constructive feedback is to foster a favorable outcome by offering advice, comments, reviews, or suggestions that are invaluable and helpful to a person. The aftermath of constructive feedback is often a boost in the process rate, improvement in human behavior, identification of any weakness, spotlighting of new perspectives, etc., and much more.
The purpose is to provide feedback to an individual in a sense that’ll pave a path toward improvements. This is a noteworthy component, as it augments personal growth on top of professional development in individuals.
3. Formal feedback
A deliberated form of feedback that’s planned and structured professionally in advance to give to an employee.
Additionally, formal feedback is much more organized, methodically documented, and secured for future reference in the business files.
Feedback sessions such as this provide a mutual platform for both the employer and the employee to have open discussions. Questions, doubts, problem areas, things going well, open questions, etc., and much more.
A formal feedback session at the job demonstrates actionable insights in accordance with the facts and figures. You can also convert form into QR Code for formal feedback collection, allowing employees to access and fill forms seamlessly during review sessions.
4. Informal feedback
Informal feedback, as the term suggests, is a casual form of catching up with employees on the work being done.
The sudden and in-the-moment kind of conversation with a person regarding their performance, behaviors, or interactions in the organization.
Informal feedback is a common form of feedback as it takes place at any time, among anyone, and can be as influential and beneficial as ineffective and unkind.
People can be more transparent with each other in this setting as no formal boundaries tie them down from speaking their minds.
5. Positive feedback
The type of feedback that every employee wants in their records. Positive feedback focuses on the strengths and values an employee contributes toward the organization’s success.
Employees that receive quality positive remarks feel appreciated and are more inclined to work toward the company’s success, thus, making them loyal. Humans are naturally motivated to do and be better after hearing some positive feedback.
Positive feedback fortifies good behaviors and helps employees polish their skills professionally.
As the saying goes, excess of everything is bad. Similarly, it’s essential to keep in mind that positive feedback shouldn’t be overused, too, as it decreases the value.
6. Negative feedback
Negative feedback is the type of feedback people usually avoid, but a balance needs to be maintained. Where there’s a negative, there’s a positive too. Negative feedback can often make people anxious or demotivated, which lowers productivity.
But it is also essential as the areas that need to be improved can be highlighted.
Negative feedback can be effective and valuable as it enables supervision of performance and alerts about the changes that should be made.
7. Quantitative feedback
The data for feedback purposes that calculates results on a numerical basis, is referred to as quantitative feedback. It assists in quantifying the aspects of a business like – customer service, product and campaign success, etc.
Quantitative feedback works by measurable outcomes and metrics. The information acquired through it is robust and reliable about employee and company performance.
The idea behind quantitative feedback is to acquire multiple answers. Quick multiple choice questions are primarily used so that it’s easy to answer and a high dropout rate can be avoided. Conclusions are then drawn based on the statistics acquired.
8. Qualitative feedback
Qualitative feedback is a non-numerical representation of comments and reviews through which individual perspectives can be understood. Organizations bring qualitative feedback into action so as to gain quality insights about the clientele and their issues or motivations.
Qualitative feedback enables a more subjective discussion about quality and performance and helps discover the ‘why’ behind quantitative results.
9. Sandwich feedback
As the term suggests, this type of feedback literally portrays a sandwich. Herein, two positive feedbacks cushion the negative feedback.
Initially, the superior delivers positive feedback and then critical or constructive feedback. After that, another positive feedback closes the whole feedback process.
Professionals more often than not prefer the sandwich feedback or hamburger method as a valuable and innovative way of tackling challenging conversations. The idea behind this type of feedback is to ease the blow of the critique by engulfing the negative remarks between two positive comments.
10. Immediate feedback
The instant feedback approach wherein reviews are provided on-demand or contextually, immediately after a learner’s action. This assists a person in deepening their understanding of things and how to improve themselves.
Immediate feedback that is provided just after the action or learning helps improve understanding. It addresses the misconceptions, reinforces the strategies, and supports in achieving a high retention rate.
Furthermore, immediate feedback enhances an individual’s confidence and self-awareness which leads the path toward increased motivation.
11. Summative Feedback
Summative feedback is given at the end of a specific period, project, training, or evaluation cycle. Its primary purpose is to assess overall performance rather than guide real-time improvement. Think of it as the “final scorecard” that sums up an employee’s achievements, skills, and areas for growth after a defined phase of work.
For example: after a 6-month project, a manager might share a performance review highlighting the employee’s contributions, quality of work, and how their efforts impacted the final outcome.
12. Formative Feedback
Formative feedback is given during a project or task to guide improvement in real time. Its goal is to help employees adjust their approach before final results are delivered.
Example: A manager suggesting changes to a presentation draft before it’s finalized.
13. Self Feedback
Self feedback is when employees evaluate their own performance, strengths, and areas for growth. It builds self-awareness and accountability.
Example: An employee reflecting on their productivity after completing a major project.
What are the 5 steps of feedback?
Here’s a simple five-step method following the LEARN Approach that HR teams and managers can use:
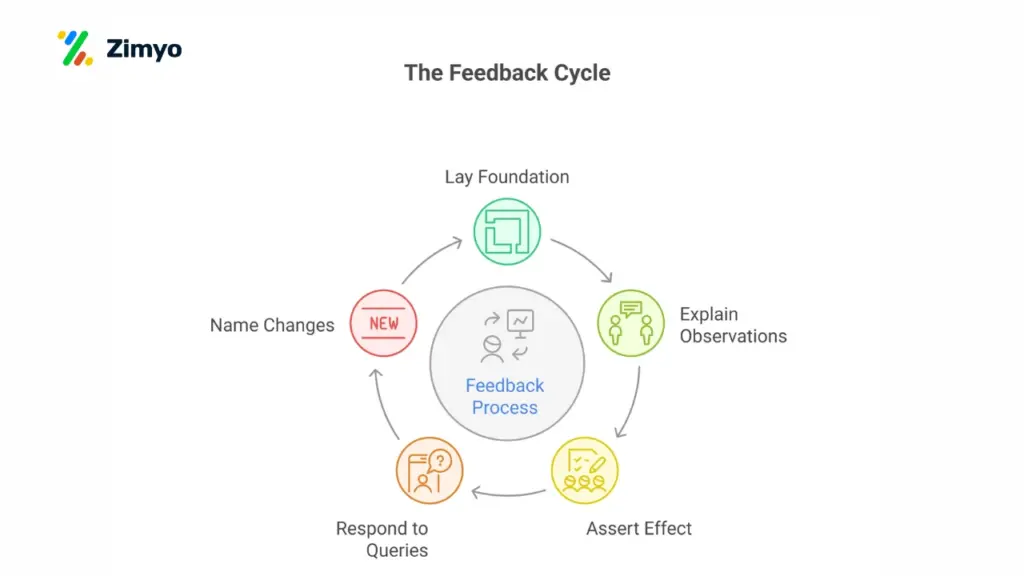
1. Lay Out a Foundation for Feedback
Start by setting the tone for the conversation. Always choose a private, distraction-free space, and explain why you’re giving feedback. This will reduce defensiveness and prepares the other person to listen.
For Example:
“I wanted to have a quick conversation about yesterday’s client meeting so we can talk through what went well and what can be improved.”
2. Explain What You Observed (As It Is)
Be factual and specific, do not beat around the bushes it will prevent misunderstandings. Try to focus on actions, behaviors, or results rather than assumptions or personal traits.
Example:
“During the meeting, you presented the sales forecast but skipped the Q2 performance summary slide.”
3. Assert Its Effect on You (or the Team/Project)
Explain the impact of their actions so they understand why it matters. This approach connects behavior to real outcomes.
Understand with an Example:
“Without that slide, the client didn’t get the full picture of our quarterly progress, which led to follow-up questions after the meeting.”
4. Respond to Any Queries
Allow the recipient to share their perspective, ask for clarification, or explain challenges they might be facing. This ensures it’s a two-way conversation, not just a lecture.
For Example:
“Was there a reason you decided to skip that part? I want to understand your thinking.”
5. Name What to Keep and What to Change
End your feedback with a clear summary. Highlight what worked well, what needs improvement and give actionable steps.
Example:
“Your confidence and clarity were excellent .. keep that up. For next time, make sure to include all slides in the sequence, even if time feels short.”
Why Feedback Matters in the Workplace
Feedback could be a strategic driver of business performance if used correctly. In workplaces where feedback is regular, balanced, and constructive, employees tend to be more engaged, productive, and show commitment to the organization’s success.
Here’s why feedback holds such a central role:
1. Aligns Employees with Company Goals
Lack of feedback can cause even high-performing employees turn in wrong direction. That is exactly why it’s important to let them know what is expected of them and how their work connects to the bigger picture- all through feedback.
2. Encourages Continuous Learning
Both formative feedback and summative feedbacks allow employees to identify skill gaps. Hence they are able to take proactive steps to improve along with fostering a culture of self-development.
3. Improves Performance and Quality
Whether it’s a positive feedback that reinforces great work or constructive criticism that addresses improvement areas. Timeliness is very important it directly impacts output quality.
4. Strengthens Trust and Communication
Regular feedback opens up a two-way communication. So that employees feel heard and valued, while managers gain better insight into employee needs.
5. It boosts Morale and Retention
Recognition-driven feedback are known to motivates employees. But also quite efficient in reducing turnover by making them feel appreciated and supported.
Feedback is all about creating a supportive environment where employees can thrive, innovate, and contribute meaningfully.
The Role of HR Teams in Effective Feedback
In modern organizations, HR teams are the architects of a healthy feedback culture. While managers are the ones giving feedback directly but HR ensures that it is consistent, fair, and strategically aligned across the company.
Here’s how HR teams contribute:
1. Designing Feedback Frameworks
HRs can develop clear policies and guidelines for delivering formal feedback, informal feedback, or even 360 performance feedback. Ensuring consistency across departments.
2. Training Managers and Leaders
Many managers are experts in their fields but that doesn’t mean they have necessarily skill in delivering feedback. What HR teams can do is conduct trainings on how to give constructive criticism meaningfully. Avoiding any biases and ensuring the message is well-received.
3. Integrating Feedback into Performance Management
HRs can ensure that feedback is tied to performance goals, skill development plans, and career progression making it actionable rather than a standalone comment.
4. Encouraging a Feedback-Friendly Culture
Through employee engagement initiatives, HR can foster an environment where self feedback and peer-to-peer input are as valued as manager-led feedback.
5. Ensuring Fairness and Transparency
HR teams maintain a documented record of feedback to support decisions related to promotions, salary hikes, or disciplinary action – eliminating disputes and bias.
We can confidently say that HR is both the guardian and the enabler of effective feedback practices. They are the ones ensuring that the process benefits employees and aligns with organizational goals.
How HR Software Makes Feedback Better
In the past, feedback was often given verbally and forgotten soon after. But in today’s digitally driven workplace, HR software ensures feedback is timely, documented, and data-backed.
Here’s how technology transforms the feedback process:
1. Automated Feedback Cycles
No more missed performance reviews or late evaluations because HR software sends reminders to managers and employees to ensure feedback happens on time.
2. Centralized Performance Records
All feedback ranging from positive feedback notes to constructive criticism are stored in a single, accessible platform. This makes it easier for HR and managers to track progress over time.
3. Pre-Built Feedback Templates
Many platforms include templates for formal feedback, formative feedback, or even summative feedback, ensuring that managers provide clear, structured, and actionable input.
4. Real-Time Recognition Features
Instant shout-outs, badges, or appreciation notes can be sent directly through the system, making informal recognition quick and visible.
5. Data Analytics and Insights
Feedback trends can be analyzed to spot common challenges, measure the effectiveness of training programs, and identify high-potential employees for future leadership roles.
6. Integration with Employee Management Tools
Feedback doesn’t live in isolation, integrated HR software connects it with goal setting, learning management, and career development, making it part of a continuous improvement loop.
Check Out Our Blog on Top HR software for Growing Businesses.
Boosting Feedback Culture with Zimyo’s Employee Engagement Software
In today’s workplaces, feedback is more than an annual performance review — it’s a continuous conversation. Zimyo’s Employee Engagement software equips HR teams and managers with the tools to make feedback timely, actionable, and meaningful. From gathering employee insights to tracking progress and fostering recognition, Zimyo helps businesses create a culture where feedback drives both performance and satisfaction.
Key Features for Effective Feedback:
- Pulse Surveys – Collect quick, frequent insights from employees to gauge morale and engagement.
- 360-Degree Performance Feedback – Gather input from peers, managers, and subordinates for a well-rounded view.
- Anonymous Feedback Channels – Encourage honest input without fear of repercussions.
- Performance Tracking – Monitor progress over time and measure the impact of feedback.
- Recognition Tools – Celebrate achievements to reinforce positive behavior and motivation.
Winding up
The importance of feedback is not only the emphasis on professional growth, but also the aspect of personal growth. This eventually all adds up to drive a positive organizational and financial outcome.
A culture of feedback rests upon the shoulders of psychological norms, where workers are interlinked. Developing and maintaining relationships, addressing the biases, having open discussions, offering constructive criticism, and highlighting the successes.
Organizations want to build and nurture a culture where the workforce feel valued and great success is accomplished through even better work. Adopting a culture with quality feedback at every stage will pave the path toward that goal.
Feedback molds every individual into the people and professionals they are—or aspire to be. A study by Gallup suggested that managers who often provide their workforce with feedback influence them to be 4 times more motivated to outperform themselves, and 3 times more engaged at work.
In today’s swift moving era, software providers like Zimyo, are keen on understanding each and every organizational and workforce requirements and are bridging the gaps between them with their robust solutions.
FAQs
What are the 3 C's of feedback?
The 3 C’s of feedback are Clear, Constructive, and Consistent – ensuring the message is easy to understand, focuses on improvement, and is delivered regularly.
What are the various types of feedback?
Common types include positive feedback, negative feedback, constructive feedback, formal feedback, informal feedback, self-feedback, summative feedback, formative feedback, and 360-degree performance feedback
What are the 7 keys to feedback?
The 7 keys are Specificity, Timeliness, Clarity, Relevance, Actionability, Balance, and Empathy – helping feedback be meaningful and effective.
What are the 3 R's of feedback?
The 3 R’s of feedback are Receive, Reflect, and Respond – encouraging active listening, thoughtful consideration, and actionable follow-up.








